Space-Based Solar vs. Conventional Solar – How Are They Different?
We all are familiar with residential and commercial solar panels. They can be found all around states like California, New York, Massachusetts, and more. The blue and black panels are very recognizable and stick out from homes or buildings with traditional rooftops.
Space-based solar, on the other hand, is a topic that even those with knowledge in home and commercial solar are not quite familiar with. So, what is solar for space like, and how is it different from conventional solar technology?
Using Solar Power in Spacecraft
Photovoltaic cells were first used on the Vanguard 1 satellite, which was launched by the US in 1958. Since then, solar technology has been greatly adapted and optimized to suit the conditions of space.
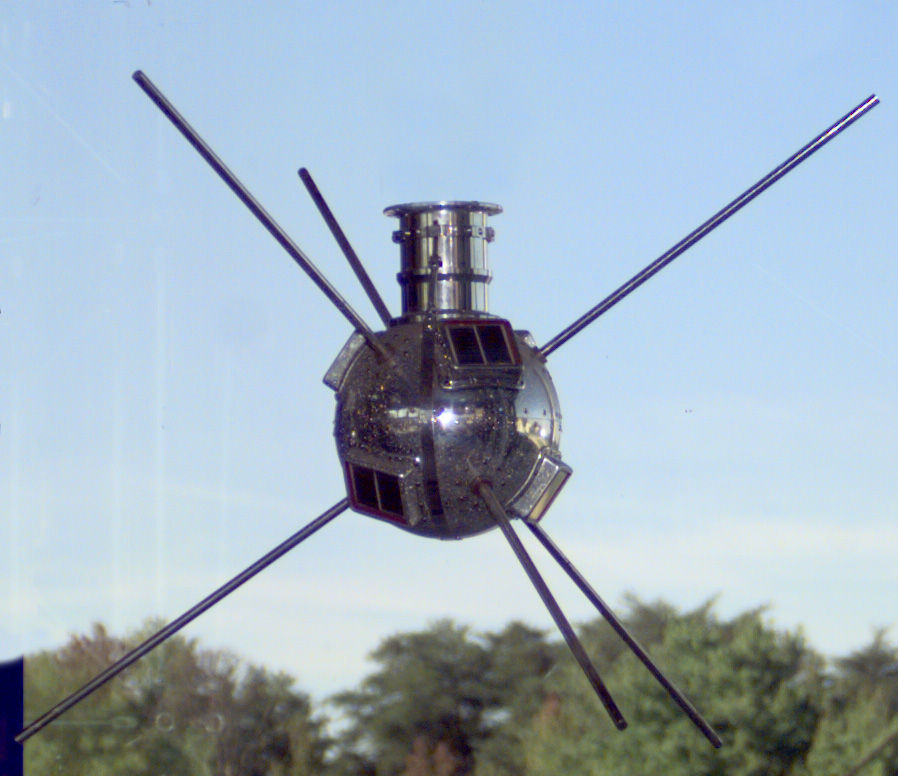 The Vanguard 1 satellite and it’s little PV cells
The Vanguard 1 satellite and it’s little PV cells
The conventional monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panels that are used in residential and commercial settings are not durable enough to withstand the extreme conditions in space like excessive heat and cold, and a constant shower of solar radiation. Because of these unique environmental factors, the solar panel technology used in space is quite different from conventional panels.
Why is solar power needed on satellites?
Spacecraft and satellites in space need a tremendous amount of energy to be operational. Before solar was a viable solution for providing this power, batteries were used. The only problem is that batteries have a set capacity, and without any means to recharge these batteries, they become useless when they run out of energy.
Solar panels paired with batteries are a much better option because they provide a constant stream of renewable energy. Right now, solar is used to provide electricity to the computer systems and other systems that are used to monitor and control various parts of the spacecraft.
The ultimate goal, however, is to use solar energy to propel spacecraft and minimize or completely remove the need for other sources of fuel. This would have serious implications for space travel in a very positive way.
What solar technology do spacecraft use?
There are two types of solar cells that are common in spacecraft:
- Silicon cells covered in thin glass, and
- Multi-junction cells made up of gallium arsenide and other similar materials.
The silicon cells that are covered with glass are pretty similar to conventional solar panels, but they are further improved to handle radiation and extreme temperatures. This type of panel can be found on the International Space Station, which currently holds the majority of solar panels found in space.
The solar cells that are made up of gallium arsenide are much more efficient, and as a result, are sometimes a better option when physical space is a concern. These panels can reach up to around 34% efficiency vs. the 15-20% that most commercial solar panels can reach.
 High-efficiency gallium arsenide panels of the Dawn satellite
High-efficiency gallium arsenide panels of the Dawn satellite
Satellites in space are also equipped with solar panels that can follow the direction of the sun to maximize their absorption of sunlight. Sun rays in space are even more abundant than on Earth, due to the absence of an atmosphere. About 55-60% of solar energy gets either reflected or absorbed on its way to Earth’s surface through clouds, gases, and dust.
The solar panels found in many satellites in space also include a folding structure that allows the panels to expand while the spacecraft is in orbit. This format is also used in the International Space Station.
Lastly, the solar panels in space do not need to convert DC electricity into AC. On Earth, your electricity all of your electronics run on AC power. This is why it is necessary to have a solar inverter to convert the base DC electricity from your panels into AC. AC power is also useful for transmitting electricity over long distances.
Because the electricity that a satellite in space or other spacecraft does not need to travel these distances, it can stay in the DC format. This also helps reduce the amount of hardware needed for these systems.
Space Solar Tech is Built More Durable and Efficient
Overall, there are many similarities between space-based solar panels and conventional solar panels. They both include cells that are made of conductive material (usually silicon) and are fit into arrays. The biggest difference has to do with the overall quality and durability of the modules.
In space, there is extreme heat, cold, and radiation. This is accounted for in space-based solar panels and naturally influences the state of the hardware. Also, NASA is constantly experimenting with different semiconductor materials for producing better solar cells for space. Gallium arsenide is one example of this, and there should be many new innovations on the way!