What Are the Negatives of Solar Panels?
Solar panels are a great way for homeowners to reduce their energy costs, increase their home value, and lower their carbon footprint.
But every energy source has its drawbacks. Nuclear is expensive, hydroelectric dams disrupt waterways, and fossil fuels are warming the planet faster than life can keep up.
In this article, we’ll explore the negatives of solar energy and things to be aware of before installing solar panels on your roof.
What is the main downside of solar energy?
With solar panel cost falling substantially over time, the main downside to solar energy is that it is intermittent. Solar panels require sunlight to produce energy, and electricity production grinds to a halt when that sunlight isn’t available.
While this isn’t much to worry about for residential solar owners with net metering or battery storage, it poses challenges to grid operators. The mismatch in solar production and peak electricity consumption forms what’s known as the “duck curve.” Or, in solar-heavy markets like California, the “canyon curve.”
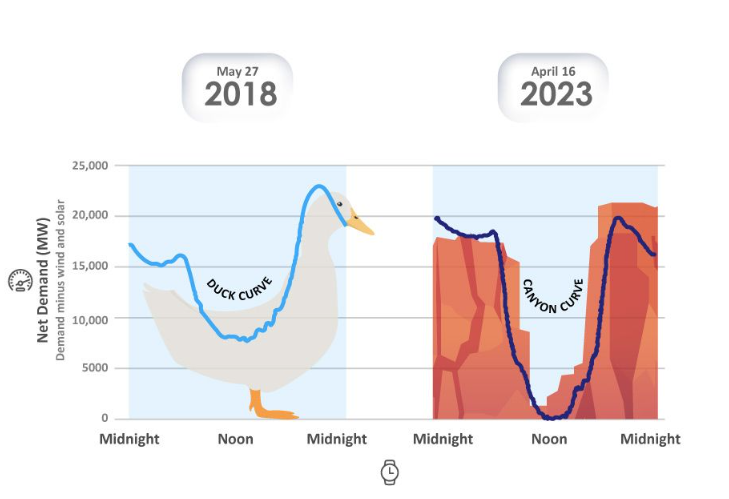
Photo courtesy of EPI.
There are two main problems with a steep canyon curve:
- It can lead to the overproduction and waste of clean solar energy during the day
- It requires baseload energy sources (like hydro and natural gas) to shutdown during the day and restart at night, which is expensive
How to flatten the duck curve
The primary solutions to this problem are various forms of load shifting and energy storage.
For instance, utilities use time of use rates to encourage homeowners to use more electricity during the day and less in the evening. And in California, the Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) approved a new solar billing policy called NEM 3.0 that makes pairing battery storage with solar panels especially beneficial.
While intermittence poses a substantial challenge to grid operators, it’s worth pointing out that solar energy is also cheaper and many times cleaner than fossil fuels. Solar panels are also incredibly versatile and can be used in various applications to increase crop production, reduce water loss, and power off-grid systems.
Next, let’s consider the pros and cons of putting solar panels on your home.
What are 3 cons of using solar panels on your home?
The three major cons of home solar are intermittence, upfront solar panel cost, and the need for storage to provide backup power.
Intermittence
Since solar power is intermittent, most home solar systems are connected to the local utility grid, which stores excess solar electricity produced during the day and provides backup power at night.
Although this is beneficial for residential solar owners (especially with net metering), it contributes to the duck curve that we mentioned above.
The main downside of solar energy is that it needs to be paired with storage or other forms of energy in order to provide a constant source of electricity.
Upfront cost of solar panels
Another con for rooftop solar is that it can be cost prohibitive. Going solar can substantially reduce your energy costs – but only if you have enough cash or good enough credit to qualify for financing.
Even with rising interest rates, financing a solar system is often more affordable than paying for utility electricity. However, you first have to be able to qualify for financing.
You typically need a 650 FICO credit score and a debt-to-income ratio (DTI) below 50% to qualify for a solar loan, which prevents many lower- and middle-income households from being able to buy solar panels.
If you want to go solar in the future, use a solar panel calculator to get a rough estimate of how much it would cost and check your DTI and FICO credit score to see if you qualify for financing. If you don’t, work on improving your credit score and DTI now so you can go solar in the future.
Need battery for backup power
The final con of solar panels is that they need to be paired with battery storage in order to provide backup power during grid outages.
When the grid goes down, solar-only systems are automatically shut off in order to protect the utility workers repairing the grid. But, if you have battery storage, your system stays on and can continue to power your house and charge your battery during the outage.
Solar panel regrets
Every home improvement project is subject to errors, oversights, and scams that can cause buyer’s remorse – and solar is no exception.
The majority of solar regrets fall into two categories:
- Entering a long-term leases and power purchase agreements (PPAs) without fully understanding the contract
- Poor installer performance and/or scams
Leases and PPAs are often advertised as “free solar” in order to lure people into signing a long-term contract that’s far less favorable than purchasing a solar system. These agreements often become troublesome when the homeowner tries to sell the house.
There are also solar owners with buyer’s remorse stemming from shoddy workmanship, customer service, or scams.
The key to avoiding solar panel regret is getting multiple quotes from trusted local installers. Better yet, use a marketplace like solar.com so you have an entire team of people advocating for your project instead of going it alone.
Connect with an Energy Advisor to discuss the pros and cons of solar for your home.








